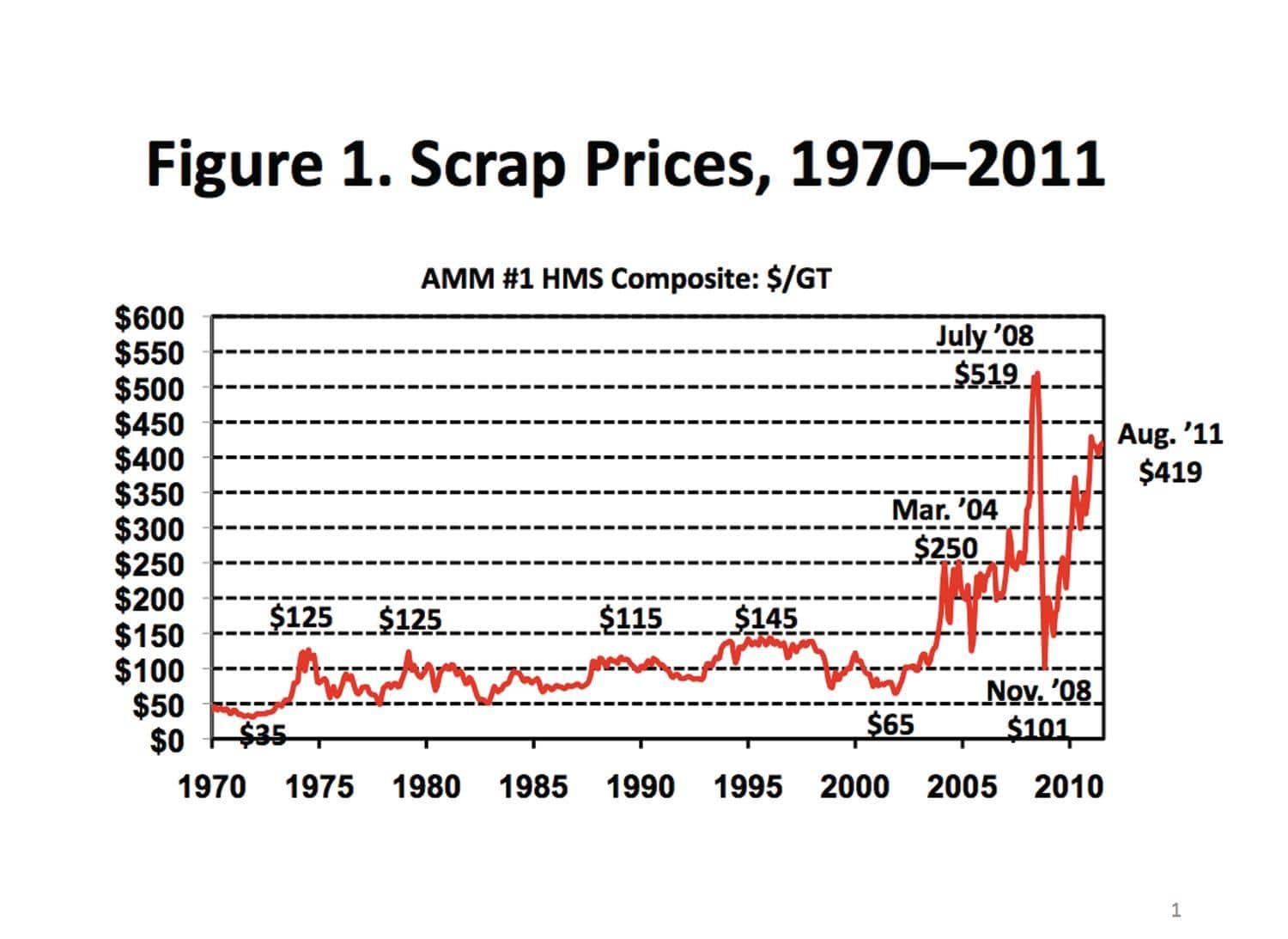
Scrap metal Economics & Value – How Are Prices Determined
Scrap metal prices are influenced by a variety of factors that reflect both macroeconomic and microeconomic conditions. Understanding these factors is important for anyone involved in the scrap metal industry, from collectors, sellers and manufacturers.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The most fundamental factor determining scrap metal pricing is the balance of supply and demand. When the demand for metals like steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals is high in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and technology, prices tend to rise.
Conversely, an oversupply of these metals can lead to a decrease in prices. For example, during periods of economic growth, the construction industry’s increased demand for materials like scrap steel and copper drives prices up. In contrast, economic downturns typically see a reduction in demand and, consequently, a drop in prices.
Quality and Purity
The quality and purity of scrap metal are critical in determining its value. Clean, uncontaminated metals are more desirable and can fetch a higher price at scrap yards.
For instance, scrap metal recyclers often pay more for metals that are free from mixed materials and corrosion. The presence of impurities can significantly reduce the scrap metal prices as additional processing is required to purify the material.
Global Market Conditions
Global market conditions play a significant role in setting scrap metal prices. Factors such as international trade policies, currency exchange rates, and economic stability influence metal markets.
For example, changes in trade policies between major metal-consuming countries can affect the availability and cost of scrap metals. Similarly, fluctuations in the value of currencies can make exporting or importing metals more or less expensive, thus impacting prices.
Economic Implications of Scrap Metal Prices
Industry Impacts
The scrap metal industry is intricately linked to various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and waste management. High scrap metal prices can lead to increased costs for these industries, which may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for finished goods.
For instance, a rise in the copper price can affect the cost of electronics and construction materials, impacting the overall economy.
Environmental and Resource Efficiency
Scrap metal recycling contributes significantly to environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. By recycling metals, we reduce the need for mining new raw materials, conserving natural resources and reducing the environmental impact of metal production.
The economic benefits of this process include energy savings—recycling metals typically consumes less energy than producing new metals from ore. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also lowers production costs, contributing to a more sustainable economy.
Job Creation and Economic Development
The scrap metal industry also supports economic development through job creation. The processes involved in collecting, sorting, processing, and selling scrap metal provide employment opportunities at various levels. From workers in scrap yards to local manufacturers using recycled materials, the industry stimulates economic activity and supports livelihoods.
Price Determination and Market Mechanisms
Market Prices and Online Resources
To determine the accurate price of scrap metal, several mechanisms and resources are utilised. Market prices for metals are often tracked and reported by commodity exchanges and online platforms.
These resources provide up-to-date information on scrap metal prices, allowing sellers and buyers to negotiate fair transactions. For example, websites that track the copper price or the price of other metals offer valuable insights into market trends and price fluctuations.

Example of scrap metal prices online
Fair Price Practices
Ensuring a fair price for scrap metal involves transparency and accurate assessment of the metal’s value. Reputable scrap metal recyclers and buyers should provide clear pricing structures and explain how prices are determined based on factors such as metal type, quality, and current market conditions.
Sellers can use these online resources to verify that they are receiving competitive offers and getting top dollar for their materials.
Current Trends and Future Outlook
Technological Innovations
Recent advancements in technology are shaping the future of the scrap metal industry. Innovations in sorting and processing technologies, such as automation and AI, are improving the efficiency and accuracy of recycling operations. These technologies help in better sorting of metals, reducing contamination, and maximizing the value extracted from scrap.
Global Trade Dynamics
The global trade of scrap metal continues to evolve, influenced by international policies and economic conditions. Countries with strict environmental regulations often import large amounts of scrap metal to meet their manufacturing needs sustainably. The dynamics of global trade affect the availability and pricing of scrap metals, with policy changes and economic shifts playing a pivotal role.
For a more in depth look at trends, see our page on scrap metal trends.
Final Points
Understanding the economics and price determination of scrap metal is essential for stakeholders across the industry. The interplay of supply and demand, quality, and global market conditions drives the scrap metal pricing.
The industry not only supports environmental sustainability and resource efficiency but also contributes significantly to economic development and job creation. Staying informed about market trends and utilizing reliable online resources can help sellers and buyers navigate the market effectively, ensuring they receive a fair price for their scrap.
As technological advancements and global trade dynamics continue to shape the industry, the future of scrap metal recycling looks promising, with opportunities for increased efficiency and sustainability.